All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Current Landscape and Overview of Gastrointestinal Health in Indonesian Children: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Background
Digestive health plays a crucial role in pediatric growth and development. Indonesia, as a developing nation, grapples with widespread infectious gastrointestinal (GI) ailments, particularly in rural areas. Concurrently, urban regions are experiencing an increase in non-infectious GI conditions due to recent socio-economic shifts. Current data on GI health among Indonesian children remains scarce and fragmented.
Objective
The objective of this scoping review was to elucidate the present state of GI health among Indonesian children under five years of age.
Methods
A scoping review was carried out to assess the current landscape of GI health in Indonesia. The review encompassed studies published between 2012 and 2022, with database searches performed on PubMed and Google Scholar from April 1st to 14th, 2022, using relevant keywords.
Results
The review identified 58 studies meeting the inclusion criteria. Analysis of these studies revealed five key themes in pediatric GI health: [1] epidemiology, [2] infectious and non-infectious GI disease, [3] diagnostic, [4] interventions, and [5] short-term and long-term effects.
Conclusion
The review identified diarrhea, gastroenteritis, colitis, soil-transmitted helminth infections, regurgitation, constipation, and colic as the most prevalent GI issues among Indonesian children under 5. The study highlights the interconnected nature of gastrointestinal diseases, malnutrition, and gut microbiota. It underscores the importance of proper dietary habits and adequate early nutrition, including both macro and micronutrients, with particular emphasis on fiber intake, in fostering a healthy gut microbiome essential for optimal GI function.
1. INTRODUCTION
Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of gastrointestinal (GI) health in overall human well-being. The influence of the gut extends beyond digestion, impacting various aspects of health, including immunity, emotional state, and cognitive function [1-4]. This connection is particularly crucial in children under five, as their digestive systems undergo rapid changes and dietary transitions. The status of GI health during this period significantly shapes a child's growth, development, and long-term health prospects. Evidence suggests that certain GI conditions may increase the risk of future physical and mental health problems, including malignancies, depression, and anxiety [5, 6]. These findings underscore the importance of investing in children's GI health to improve overall health outcomes and socio-economic conditions [7].
Indonesia, as a developing nation, faces a complex landscape of GI health challenges. While rural areas continue to struggle with infectious GI diseases, urban centers are seeing a rise in non-infectious conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and reflux disease. A government survey from 2010 revealed that GI problems like diarrhea, gastroenteritis, and colitis ranked fifth, while dyspepsia ranked sixth among the top ten outpatient diagnoses [8]. With an overall prevalence of 9%, infectious and non-infectious diarrhea has become a leading cause of hospitalization and mortality, particularly in children under one-year-old [9].
To address these concerns, Indonesian authorities have implemented several public health initiatives. Programs, such as PBHS (Healthy and Clean Living Behavior), the Diarrhea Control Program, GERMAS (Healthy Living Community Movement), and STBM (Community-Based Total Sanitation), have shown some success in mitigating GI problems in certain areas [10, 11]. For instance, GERMAS and STBM have been effective in improving access to clean water and sanitation. By 2017, these programs had been introduced in 39,616 villages across 23 provinces. A survey by Utama in 2020 confirmed their positive reception, with 47% of respondents stating GERMAS was implemented very well and an additional 39% reporting it was quite well implemented [12, 13]. However, due to Indonesia's complex geography, inadequate health infrastructure in rural areas, and scarcity of healthcare professionals, GI diseases remain a significant health challenge [14].
The research landscape regarding children's GI health in Indonesia has been expanding, with increased attention from donors and academic institutions. However, comprehensive studies that provide a holistic picture of the current GI health conditions of children in Indonesia remain scarce. This scarcity is largely due to limitations, such as small sample sizes, narrow age group focus, and a lack of longitudinal studies to determine long-term effects on growth and development.
This study aims to address this knowledge gap by conducting a scoping review to describe the current GI health conditions of children under five years old in Indonesia. In collaboration with experts from an Indonesian academic institution, we hope to uncover GI health conditions, problems, and issues that can inform future research directions. By synthesizing existing knowledge and identifying key areas for further investigation, this review seeks to contribute to the improvement of GI health among Indonesian children, ultimately enhancing their overall health and well-being.
2. METHODS
This study employed a scoping review methodology, utilizing PubMed and Google Scholar as primary literature databases. To focus on a critical developmental period, this study concentrated on children under five years old, aiming to elucidate current gastrointestinal (GI) health conditions in this vulnerable age group. The research team conducted a comprehensive literature search between April 1st to 14th, 2022, employing key phrases, such as “gastrointestinal health”, “children”, “under five”, and “Indonesia”. When necessary, Boolean operators were applied to refine search results. The team screened abstracts for relevance and compiled pertinent studies in a shared spreadsheet, facilitating duplicate identification and removal.
The study adhered to specific inclusion criteria [1]: focus on children under five years [2], studies conducted in Indonesia [3], availability of full-text articles [4], publications in English or Indonesian [5], research published within the last decade (2012-2022), and [6] official government reports. Conversely, exclusion criteria encompassed [1] lack of full text in English or Indonesian [2], non-peer-reviewed works (such as preprints or internal academic publications), and [3] studies not including children under five.
Upon completion of the search period, the research team, in collaboration with pediatric experts from Jakarta, Indonesia, collected, organized, and evaluated a total of 58 relevant studies. The specialists assessed the practical relevance and validity of the information presented in these studies. Significant findings were synthesized and categorized into five fundamental themes crucial to understanding GI health in Indonesia [1]: epidemiology [2], infectious and non-infectious GI diseases [3], diagnostic approaches [4], interventions, and [5] short-term and long-term impacts (Fig. 1).
3. RESULTS
3.1. Theme 1: Epidemiology of Gastrointestinal Health in Indonesia
The state of gastrointestinal (GI) health is in constant flux, shaped by the ongoing interplay between diet, gut microbiome, hygiene practices, and socioeconomic factors. As the most populous developing nation, Indonesia grapples with a rising incidence of both infectious and non-infectious GI ailments. A 2017 national survey revealed that diarrhea, gastroenteritis, and colitis ranked fifth among the most prevalent reasons for outpatient visits in Indonesia. Diarrhea alone affected over 1 million patients, with 90,000 cases involving children under five years old [11, 15]. Common pathogens included Rotavirus, E. coli, Shigella spp, and Entamoeba histolytica, mirroring findings from a comparable study on Ghanaian children [16, 17].
In recent years, Indonesia has witnessed an uptick in non-infectious GI disorders, particularly functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs). A 2019 cross-sectional study in Jakarta, analyzing 1800 questionnaires, found that 11.5% of respondents reported FGIDs. These included functional abdominal pain (5.8%), functional dyspepsia (3.3%), irritable bowel syndrome (2%), and abdominal migraine (0.4%) [18]. Dyspepsia was another frequent cause of outpatient visits, with a study on 550 dyspepsia patients revealing gastritis in 44.7% and duodenitis in 6.5% of cases [14]. It is worth noting that comprehensive epidemiological data on pediatric GI diseases in Indonesia, especially for children under 5, remains scarce, with most studies focusing on adolescent populations.
Beyond specific GI disorders, a child's digestive health can be further compromised by factors, such as malnutrition and socioeconomic disadvantage. Indonesian children under 5 often face dietary challenges, including infrequent consumption of animal proteins, fruits, and vegetables, as well as micronutrient deficiencies [19]. Families in rural areas or with lower educational attainment are more likely to have malnourished children compared to their urban or more educated counterparts [15]. A summary of the relevant studies is presented in Tables 1 and 2.
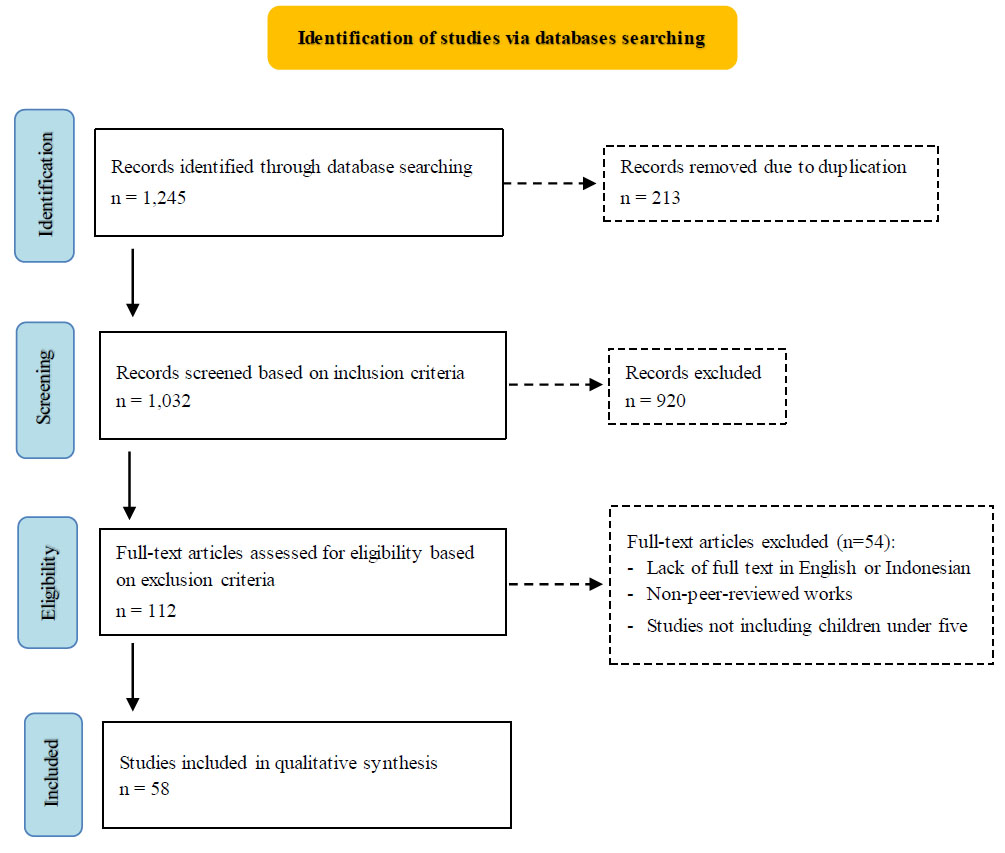
Flow chart of study selection.
| Study (Author, year, country) | Study Design | Sample Size (n)* | Methods | Gastrointestinal Problem Identified | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kurscheid et al., 2020, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 417 children (2-5 years) | Stool analysis via faecal floatation | Infectious | 35.2% positive for soil-transmitted helminths: 121 A. lumbricoides, 9 T. trichiura, 26 Hookworm |
| Agustina et al., 2013, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 274 children (12-59 months) | Interviews, observations, anthropometric measurements | Infectious and malnutrition | Diarrhea prevalence: 17% (12-23 months), 8.5% (24-35 months), 6.2% (36-47 months), 4.4% (48-59 months). Stunting: 32.1%, Underweight: 23.4%, Wasting: 9.5% |
| Utsumi et al., 2021, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 966 stool samples (1-191 months, 89.5% < 5 years) | PCR of stool samples | Infectious | 12.3% positive for norovirus. Higher prevalence in children under 2 (n=101) vs. over 2 (n=18) |
| Nirwati et al., 2019, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 406 stool samples (< 5 years) | Sequencing and genotyping of stool samples using qRT-PCR and QIAGEN | Infectious | 18.4% positive for Norovirus, 54.9% for Rotavirus, 7.1% mixed infections |
| Agustina et al., 2014, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 18,865 children (<5 years) | Indonesia Demographic Health Survey (IDHS) Data | Infectious | Diarrhea prevalence: 14.8% (under 2), 10.1% (2-4 years) |
| Nirmawati, 2016, Indonesia | Observational and cross-sectional | 4235 diarrheal stool samples (<5 years) | Enzyme immunoassay of stool samples | Infectious | 86% of cases in children under 24 months. Rotavirus positives: 359 (0-5 months), 795 (6-11 months), 810 (12-23 months), 256 (24-59 months) |
| Mulyani et al., 2018, Indonesia | Cross-sectional | 4311 children (under 5, over 5 years) | Enzyme immunoassay of stool samples | Infectious | 4013 stool specimens tested over 5 years, 1950 (48.7%) cases detected |
| Author, Year | Journal | Participant Condition | Number of Participants | Reported Microbe Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ley et al., 2006 | Nature | Obesity | 12 obese, 2 lean | Increased Firmicutes, decreased Bacteroidetes in obese individuals |
| Smith et al., 2013 | Science | Kwashiorkor | 317 Malawian twin pairs | Lower diversity, predominantly Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and anaerobic Firmicutes in malnourished children |
| De Palma et al., 2017 | Science Translational Medicine | Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) | 30 IBS patients, 25 healthy controls | Increased Bacteroides, decreased Akkermansia in IBS patients |
| Yang et al., 2017 | Science | Recurrent Salmonella infection | Mouse model | Increased Enterobacteriaceae, decreased beneficial commensals |
| Prafianti et al., 2022 | International Journal of Nutrition, Pharmacology, Neurological Diseases | Stunting | 30 stunted, 30 normal children | Decreased Prevotella 9 in stunted children |
3.2. Theme 2: Infectious GI Diseases and Non-infectious GI Diseases
Bacterial and helminth-induced gastrointestinal infections remain a significant global health concern, with younger individuals at heightened risk [20, 21]. In developing nations like Indonesia, these issues are particularly acute. A 2014 study by Tan et al. estimated that about 200 million people across 31 provinces were at risk of Soil-Transmitted-Helminth (STH) infections [22]. A 2020 epidemiological study in Semarang, Central Java, found that nearly one-third of 6,466 participants from 2,195 households had active STH infections [23]. While affecting both children and adults, childhood STH infections are more devastating, potentially leading to nutritional, physical, and cognitive impairments that perpetuate poverty cycles [23, 24]. School-age children face the highest risk of STH infections and their long-term consequences [23].
Pediatric gastrointestinal infections in Indonesia vary by age group. Bacterial pathogens like Salmonella spp. (causing typhoid fever) and Shigella spp. (causing dysentery) are common, especially in children aged 2-4 years. Escherichia coli, particularly enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic types, frequently cause diarrhea in infants and young children, exacerbated by malnutrition and poor sanitation.
Viral infections, notably Norovirus and Rotavirus, are significant contributors to gastroenteritis in children and adults. A study by Nirmawati et al. found that out of 406 patients, 18.47% tested positive for Norovirus and 54.93% for Rotavirus. These infections, causing dehydration, diarrhea, vomiting, and fever, can disrupt children's nutritional absorption. While affecting children aged 0-60 months, Rotavirus infections clustered in the 7-24 month age group, and Norovirus in the 7-36 month group.
Rotavirus remains the leading cause of severe diarrhea globally, particularly affecting Indonesian infants and young children aged 6-24 months. Norovirus peaks in prevalence among children aged 7-36 months, as reflected in acute gastroenteritis hospitalization rates. Both viruses can cause severe dehydration, complicating clinical management.
Recent research has focused on gut dysbiosis, where antibiotic use and gastrointestinal infections alter the gut microbiome. This disturbance in the complex genetic, environmental, and microbial interactions may lead to chronic gastrointestinal pathologies like inflammatory bowel disease and colitis [24, 25]. While data from Indonesia is limited, studies suggest that certain gastrointestinal infections, such as Salmonella Typhi-murium, can induce chronic intestinal inflammation, disrupting the protective barrier function of the human gastrointestinal tract [26].
Non-infectious gastrointestinal conditions like gastro- esophageal reflux disease (GERD), constipation, and functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) significantly impact children under 5. Their immature GI function, including low levels of lipase, bile salts, and amylase during the first 6 months, predisposes them to these conditions [27]. Infants are particularly susceptible to regurgitation, constipation, and colic, which may lead to FGID symptoms later in life [28, 29]. A 2015 estimate suggested prevalence rates of 20% for infantile colic, 15% for functional constipation, and 30% for regurgitation [29]. Interestingly, a survey of Indonesian general practitioners revealed a weak understanding of functional constipation symptoms, proper toilet training education, and appropriate management [30].
Growing evidence suggests a correlation between gut microbiota alterations and FGI development. Gut hypomotility and dysbiosis can lead to GI dysmotility. Studies have reported that germ-free mice given fecal matter from IBS-D patients exhibited intestinal barrier impairment, immune gut dysfunction, and altered gut microbiota [31-34]. Gut microbe-produced molecules like short-chain fatty acids, serotonin, and tryptamine modulate GI physiology, and patients with gut dysbiosis often display FGID symptoms, including delayed gut transit and smooth muscle contraction/relaxation problems [32-36].
Probiotic use shows potential in FGID treatment and prevention. Infant supplementation with lactobacilli, particularly Lactobacillus reuteri, in the first weeks after birth significantly reduced regurgitation and colic-related crying while increasing daily stool passage [28]. These findings highlight the importance of nutrition in modulating gastrointestinal function and offer promising avenues for managing and preventing functional GI disorders in the future.
3.3. Theme 3: Updates on GI Treatment and Diagnostics
Indonesia's population has been faced with an uptick in both infectious and non-infectious gastrointestinal ailments in recent years. Diarrhea affects over 17% of children under five, highlighting a significant health concern [37]. This rising incidence necessitates improved diagnostic and treatment capabilities. Currently, diarrhea diagnosis primarily relies on patient history and physical assessment, supplemented by additional tests, such as colonoscopy, endoscopy, blood analysis, stool examination, and microscopy, to confirm the diagnosis in pediatric cases [14, 38].
The field of gastroenterology in Indonesia has expanded to incorporate various diagnostic approaches. These include scoring systems like Rome IV and GERD-Q, non-invasive techniques, such as stool tests, PET CT scans, and H. pylori antigen detection, as well as invasive procedures, including endoscopy, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and ultrasonography. Notably, endoscopic services are now available in more than 313 hospitals nationwide [37, 39].
Despite these advancements, there is a notable lack of research examining the availability and accuracy of these diagnostic methods in Indonesia's rural regions. This gap in knowledge presents an important area for future investigation to ensure equitable access to accurate gastrointestinal diagnostics across the country.
3.4. Theme 4: Interventions
Indonesia has implemented various strategies to manage diarrhea, including the LINTAS Diare program (Lima Langkah Tuntaskan Diare). This five-step approach aims to treat diarrhea, enhance household knowledge, and provide patient monitoring. The initial step involves oral rehydration therapy, with dosage based on symptom severity. Next, zinc supplementation is recommended to reduce condition severity by promoting gastrointestinal wall re-epithelialization. Maintaining food intake and/or breastfeeding is crucial to prevent further nutrient and weight loss. Antibiotics may be prescribed if infection is indicated, though improper use can lead to dysbiosis. Finally, patients or caregivers receive education on home treatment and when to seek hospital care [40].
Numerous studies have recognized diet as a crucial factor influencing gastrointestinal composition and function [41, 42]. Beyond gut health, adequate nutrition plays a vital role in children's physical growth and neurodevelopment [43-45]. In Indonesia, a lack of diverse macro- and micronutrients from monotonous diets significantly contributes to poor child growth, emphasizing the importance of dietary variety [46,47]. Studies by Sari et al. and Torlesse et al. found that households with grain-heavy diets lacking adequate animal protein and vegetables had an increased odds ratio of 1.21 for stunting [45, 46]. A 2021 study by Damayanti et al. further highlighted persistent poor dietary habits among many Indonesian children [47].
Recent research has focused on the interaction between specific food sources and overall GI function, though such findings are less documented in Indonesia. Growing evidence suggests that early adequate nutrition is crucial for establishing a healthy gut microbiota, supporting optimal GI function. Ley et al. demonstrated that breastfed infants have higher proportions of beneficial lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, as well as increased sIgA in stools (a marker of good gut health), compared to formula-fed infants [48]. The timely introduction of solid foods during weaning is well-documented as a primary driver of gut microbiota maturation [41, 18].
Fiber intake is known to offer numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of weight gain, cardiovascular disease, and elevated cholesterol while improving gut health and digestive function [49,50]. High-fiber snacks for children can decrease the risk of painful constipation, promote healthy gut microbiota, and are often associated with better overall diet quality due to their sources (vegetables, fruits, whole grains) [50, 51]. However, fiber intake in Indonesia remains low. A study by Prafianti et al. in the Asmat district of Papua found that over 90% of children consumed fiber below the recommended dietary allowance (1.63 g/day) [52].
Recent research has identified a correlation between gut microbiota composition and child growth. The genus Prevotella 9 appears more abundant in normal-weight children and significantly lower in stunted children. Its levels correlate with dietary fiber intake, suggesting that alterations in gut microbiota may affect nutrient absorption in children [53].
3.5. Theme 5: Short and Long-term Impact
Imbalances in gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can have both short-term and enduring impacts on children's health. Research has demonstrated that changes in gut microbiota can significantly influence the immune system. The host's innate immunity is affected by both healthy and dysbiotic gut microbiota through various microbial components and their metabolic products. Dysbiosis may interfere with the host's capacity to identify microbial signatures, potentially altering immune responses. Bacterial interactions also affect other receptors, such as TLR2. A prime example is the oral anaerobe Porp- hyromonas gingivalis, which intensifies inflammation by altering the oral microbiota. This bacterium modifies host immune responses by encouraging MYD88 breakdown, thereby suppressing immunity while sustaining inflam- mation through the interplay between TLR2 and the C5aR complement receptor [54, 55].
The relationship between gut microbiota and cognitive development has also been observed. Studies suggest that gut microbiota plays a crucial role in early-life brain development, leading to lasting behavioral effects. Research has shown that specific bacterial compositions at one year of age can predict cognitive abilities at age two. For instance, clusters with high Faecalibacterium levels (C1) were associated with lower cognitive performance (72nd percentile), while those with high Bacteroides levels (C2) correlated with higher performance (90th percentile). Interestingly, greater alpha diversity at age one predicted poorer cognitive outcomes at age two, as measured by ELC, visual reception, and expressive language scales. This finding contradicts the usual understanding that low alpha diversity in infancy typically links to negative health outcomes, such as type 1 diabetes and asthma, while high diversity is often seen as indicative of a more mature, adult-like microbiome [56].
Globally, malnutrition in its various forms continues to be a significant health concern for children. Stunting affects over 150 million children under five, while obesity impacts 40 million [57]. In Indonesia, a complex nutritional landscape exists, characterized by the simultaneous presence of undernutrition and over- nutrition. Some researchers, including Rah (2021), have identified a “triple burden” of malnutrition, which encompasses micronutrient deficiencies. This is evidenced by the prevalence of anemia in one out of every four adolescent girls [58]. While multiple factors contribute to these nutritional issues, including dietary habits, genetic predisposition, and socioeconomic conditions, the composition of a child's gut microbiome has emerged as a critical influencing factor [59, 60].
The interplay between gastrointestinal (GI) diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and intestinal microbial communities forms a complex, self-perpetuating cycle. Dietary choices significantly shape the microbial landscape in children's digestive systems. Research indicates that infants nourished through breastfeeding exhibit elevated populations of B. longum subsp. infantis and Lactobacillus acidophilus when compared to their formula-fed counterparts [59]. Iddrisu et al. observed that alterations in gut microbiota composition, specifically an increase in proteobacteria coupled with a decline in bifidobacterium and lactobacillus, correlate with a higher incidence of diarrheal episodes. These frequent bouts of diarrhea often contribute to malnutrition. Moreover, persistent diarrhea can impair the GI tract's ability to absorb essential nutrients, potentially leading to both physical and cognitive developmental issues [57, 60]. Further insights from the study by Smith et al. revealed that children suffering from kwashiorkor or similar malnutrition disorders typically possess an under- developed gut microbiome. This immature microbial ecosystem is characterized by a predominance of Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and anaerobic Firmicutes, along with reduced overall diversity. These findings underscore the pivotal role that gut microbiota plays in the emergence and progression of malnutrition [61, 62].
Obesity and imbalances in gut microbiota can contribute to the development of obesity. The microbial communities in our digestive system play a crucial role in regulating organ permeability and the body's ability to absorb nutrients. Research by Patterson and colleagues revealed that alterations in the microbiome can lead to enhanced energy extraction and increased fat production. When these processes become excessive, they may trigger tissue inflammation and reduce insulin sensitivity, potentially culminating in obesity [63, 64]. Jumpertz et al. highlighted the distinct differences in microbial populations between individuals with and without obesity. Their findings showed that obese subjects tended to have a higher ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroides, while the opposite was observed in healthy individuals. Corroborating studies have also noted a greater prevalence of potentially harmful microbes and those involved in short-chain fatty acid synthesis, specifically Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria, in individuals with obesity [65, 66]. These observations highlight the intricate interplay between gut microorganisms and nutritional status in pediatric populations. Notably, children under the age of five who experience either malnutrition or obesity often exhibit reduced physical growth (as measured by weight and height) and demonstrate impaired cognitive abilities when compared to their healthy peers. This underscores the far-reaching impacts of nutritional imbalances and altered gut microbial compositions on overall child development.
3.6. Technological Applications in GI Health Management
Recent advancements in healthcare technology offer promising applications for improving GI health management in Indonesian children. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques show particular promise in this field. For instance, lightweight Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models could be adapted for early prediction of GI diseases based on symptoms and risk factors, potentially enabling earlier interventions [67]. ML algorithms have also demonstrated the potential to enhance the accuracy of diagnosing complex GI conditions, which could be particularly valuable in resource-limited settings [68]. In the realm of data management, blockchain technology presents an opportunity to improve the security and accessibility of children's health records, ensuring continuity of care for chronic GI conditions [69]. This could be especially beneficial in a geographically diverse country like Indonesia. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with edge computing offers possibilities for real-time monitoring of severe GI conditions or tracking nutritional status in remote areas [70]. This technology could help bridge the gap in healthcare access between urban and rural regions of Indonesia. Advanced imaging techniques, such as multi-modality image fusion, could improve the diagnosis of complex GI disorders in pediatric patients [71]. Lastly, the implementation of decision support systems, such as those based on the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), could assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions about GI health management strategies [72]. While these technologies show promise, their implementation in the context of GI health management for Indonesian children requires careful consideration of infrastructure limitations, cost-effectiveness, and cultural appropriateness. Future research should focus on adapting these technologies to the specific needs and constraints of the Indonesian healthcare system.
4. DISCUSSION
Child gastrointestinal health is a multifaceted issue, intricately linked to socio-economic factors, dietary behaviors, and cultural norms. Developing countries like Indonesia continue to grapple with various gastrointestinal conditions, particularly those related to infectious causes or nutritional deficiencies. The 2018 Basic Health Research (RISKESDAS) reported that 17.7% of children under 5 in Indonesia had substandard nutritional status (3.9% very poor, 13.8% poor), falling short of the 2019 national developmental goals [15, 73]. The prevalence of infectious diarrhea increased from 4.5% in 2013 to 6.8% in 2018. Moreover, RISKESDAS data showed high diarrheal prevalence, with 91,413 cases in children under 5 in 2018, followed by soil-transmitted helminth infections and gastroenteritis, primarily caused by Rotavirus and Norovirus [15,23,74-79]. Comparatively, Malaysia reported a lower diarrhea prevalence of 4.4% in children under 5. Globally, diarrhea accounts for over 500,000 deaths and 1.7 billion cases in children under 5 annually [80-82]. Gastroenteritis is responsible for over 10% of pediatric deaths worldwide, with Rotavirus being the primary cause.
Sari et al. highlighted the importance of socio-economic capability and nutritional knowledge in preventing stunting. Their odds ratio analysis showed that greater household expenditure on animal products (0.87; 95% CI = 0.85–0.90; P < 0.0001), vegetables (0.86; 95% CI = 0.84–0.88; P < 0.0001), and non-grain foods (0.85; 95% CI = 0.83–0.87; P < 0.0001) serves as a protective factor against stunting [45].
Gastrointestinal (GI) problems differ significantly between children under and over one year of age. Infants under one typically experience functional issues like colic, regurgitation, and constipation due to immature digestive systems. The transition to solid foods and gut microbiome maturation plays a crucial role in their GI function development. Children over one year face a broader range of GI problems, including infectious gastroenteritis, which is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, especially in low- and middle-income countries with limited access to clean water and sanitation.
The WHO World Health Statistics Report (2022) identified inadequate water, sanitation, and hygiene as prominent environmental risk factors, with at least 2 billion people lacking properly managed water services and 2.3 billion lacking basic handwashing facilities at home [83]. Studies in Indonesia have linked poor hygiene practices to infectious diseases like diarrhea and malnutrition [46,84]. Agustina et al. found that unhygienic weaning practices in East Jakarta often lead to pathogen contamination, including enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), which is significantly associated with diarrhea and weight faltering [85, 86]. Poor sanitation facilities contribute to inadequate handwashing and improper waste disposal, increasing the risk of water-borne diseases [28].
Non-infectious gastrointestinal conditions, such as GERD, functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), food allergies, and constipation, are gaining attention in pediatric gastrointestinal health discussions. Common food allergies in children under 5 include cow's milk, chicken, egg, and chocolate [87, 88]. These conditions can predispose children to FGID symptoms later in life and increase the risk of impaired nutrient absorption and growth faltering [29, 87]. Recent data suggests limited knowledge among Indonesian pediatricians regarding the diagnosis and management of conditions like constipation [30]. This aligns with findings from Saudi Arabia, where Alshehri et al. noted the challenges in diagnosing FGIDs due to vague and non-specific symptoms [89]. The scarcity of knowledge and research on FGIDs may contribute to barriers to identifying and treating these conditions [90]. The burden of these seemingly harmless conditions is believed to be rising, with psychiatric factors known to exacerbate gastrointestinal pathologies. Nearly 40% of Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome (IBS) patients seeking medication have anxiety or depressive disorders [74, 91]. The COVID-19 pandemic may exacerbate this situation due to social isolation [89, 92].
Modern society recognizes the importance of proportional and adequate nutrition for healthy living [95]. However, poor socioeconomic status is often linked to poor dietary knowledge and habits [91], a common finding in Indonesia. RISKESDAS examined 86,753 children under 5, classifying 3-4% as malnourished, 13% as under- nourished, 7-8% as overweight, and 11-12% as stunted [15]. Sufyan et al. demonstrated significant associations between nutritional knowledge and factors, such as sex, educational field, expertise, and parental income level, with higher income conferring a 2.76 times increase in nutritional knowledge. Knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) regarding diet affect children's health [93, 94]. Among adolescent girls, increased KAP was positively associated with height-for-age z-scores (HAZ), suggesting that KAP improvement combined with effective nutritional interventions can reduce risks of poor growth and anemia [91]. In the under-5 age group, improved knowledge about the importance of the first 1000 days of life significantly increases attitudes and practices associated with healthy dietary habits (p<0.001) [94]. However, exclusive breastfeeding rates during the first 5 months remain low (75%), potentially impacting physical, cognitive, and microbiota maturation. The inability to produce breast milk is cited as a primary reason for not providing exclusive breastfeeding [15]. Maternal knowledge about nutritional issues, such as folate intake in infants, correlates with better attitudes and practices, which, in turn, correlate with maintaining satisfactory serum folate levels [89]. Unfortunately, dietary diversity remains low, with only 60.5% of children aged 20-23 months consuming a balanced diet of grains, dairy, red meat, and vegetables [15] (Fig. 2).
The studies reviewed offer valuable insights into the gastrointestinal health of Indonesian children, with several strengths notable across the literature. Many of the epidemiological studies, such as by Agustina et al. (2014), boast large sample sizes, enhancing the reliability of their findings. The use of standardized diagnostic methods, including PCR and enzyme immunoassay, lends credibility to the results. Furthermore, the inclusion of diverse geographical regions within Indonesia provides a more comprehensive picture of the country's GI health landscape.
However, these studies are not without limitations. The predominance of cross-sectional designs limits our ability to draw causal inferences, a significant drawback when trying to understand the complex interplay of factors affecting GI health. There is also a potential for selection bias in hospital-based studies, which may overestimate the prevalence of certain conditions. The scarcity of longitudinal data on long-term outcomes is a notable gap in the current body of research. Additionally, there appears to be an underrepresentation of studies focusing on non-infectious GI conditions, potentially skewing our understanding of the full spectrum of GI health issues facing Indonesian children.
Despite these limitations, integrating the findings reveals several consistent themes. Infectious GI diseases, particularly diarrhea and helminth infections, remain prevalent and of significant concern. However, there is a growing recognition of the importance of non-infectious conditions, such as functional gastrointestinal disorders. A consistent association between malnutrition and poor GI health is evident across studies, highlighting the interconnectedness of nutritional status and gastrointestinal well-being. Moreover, there is mounting evidence supporting the crucial role of gut microbiota in both infectious and non-infectious GI conditions.
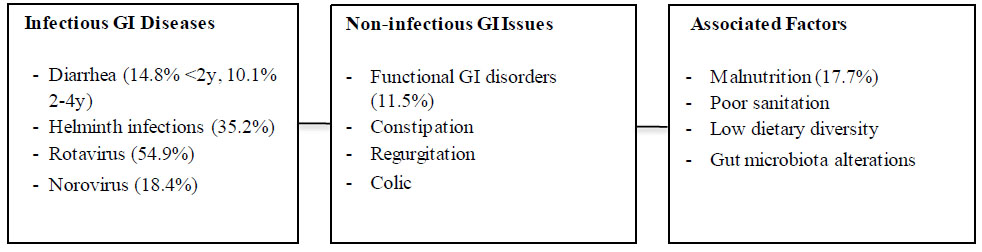
GI health in indonesian children: key findings.
Note: Percentages indicate prevalence where available. Further research is needed on non-infectious conditions.
| Study (Author, year, country) | Type | Sample size (n)* | Methods | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RISKESDAS* | Diarrheal Prevalence | 91,413 children <5 years | Interview-based assessment | 20.5% diagnosed with diarrhea; peak prevalence in the 12-23 month age group |
| Malnutrition | 86,753 children <5 years | Weight-for-age comparison with 2005 WHO standards | 3-4% classified as malnourished; additional 13% deemed undernourished | |
| Overweight | 86,753 children <5 years | Weight-for-length comparison with 2005 WHO standards | 7-8% categorized as overweight | |
| Stunting | 86,753 children <5 years | Length-for-age comparison with 2005 WHO standards | 11-12% identified as stunted | |
| Breastfeeding Practices | 7,415 infants <5 months | Interview-based survey | 74.5% exclusively breastfed; main barrier: perceived insufficient milk production | |
| Dietary Diversity | 12,776 infants <23 months | Interview on consumption of grains, dairy, red meats, and vegetables | Dietary variety increases with age: 29.8% (6-11 months) to 60.5% (20-23 months) |
Interestingly, some apparent contradictions emerge from the literature, particularly in the reported prevalence rates of diarrhea. These discrepancies may be attributed to differences in study settings (rural vs. urban), seasonality of data collection, or varying definitions of diarrhea used across studies. It is hypothesized that socioeconomic factors may explain some of these differences, not only in the prevalence of infectious GI conditions but also in non-infectious ones.
This critical appraisal underscores several crucial research gaps. There is a pressing need for more data on non-infectious GI conditions in Indonesian children under 5, as well as longitudinal studies examining the long-term impacts of early GI health issues. Furthermore, research on effective interventions specifically tailored to the Indonesian context is lacking. Addressing these gaps through more robust, longitudinal studies and standardized approaches to studying GI health in Indonesian children would significantly advance our understanding and inform more effective interventions and policies.
This research faced significant constraints in identifying relevant studies within Indonesia. Many epidemiological investigations in the country are published in local journals or university repositories that lack peer review and are not indexed in PubMed. Locating these studies necessitates time-consuming manual searches via Google. While the Indonesian government conducts annual health surveys through RISKESDAS Table 3) to provide an overview of population health, the crucial role of gastrointestinal (GI) health in child development suggests the need for a specialized medical report focusing on this area. Such a targeted report could significantly contribute to improving the nation's overall health status. To enhance our understanding of children's GI health in Indonesia, future research would benefit from expert interviews involving a diverse range of healthcare professionals, including pediatricians, internists, clinical nutritionists, and general practitioners.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
This scoping review has highlighted the complex landscape of gastrointestinal health in Indonesian children under five years old. The key findings include a high prevalence of infectious GI diseases, particularly diarrhea and helminth infections, alongside an emerging importance of non-infectious GI conditions. A strong association between malnutrition, poor sanitation, and GI health issues has been consistently observed, highlighting the interconnected nature of these challenges. The growing evidence on the role of gut microbiota in both infectious and non-infectious GI conditions opens new avenues for understanding and addressing these health issues. However, limitations in the current research, including a scarcity of data on non-infectious GI conditions, the predominance of cross-sectional studies, and the lack of standardized definitions across studies, constrain our ability to draw definitive conclusions.
Moving forward, several critical research directions emerge. Longitudinal studies are needed to examine the long-term impacts of early GI health issues, while more comprehensive investigations into non-infectious GI conditions in Indonesian children are warranted. Future research should explore interventions targeting both nutritional status and GI health, investigate the potential of probiotic interventions, and assess the feasibility of technological applications in GI health management. By addressing these research gaps, we can develop a more nuanced understanding of GI health in Indonesian children, informing more effective interventions and policies. Ultimately, a holistic approach that considers the complex interplay of biological, social, and environmental factors will be crucial in improving the gastrointestinal health and overall well-being of Indonesian children.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
MK, PGK, and AD contributed to the conception and design of the study. TS and EW collected the data. RWB and CD carried out data analysis and interpretation of results. MY drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
| GI | = Gastrointestinal |
| FGIDs | = Functional gastrointestinal disorders |
| STH | = Soil-Transmitted-Helminth |
| ML | = Machine Learning |
| CNN | = Convolutional Neural Network |
| AHP | = Analytic Hierarchy Process |


